Revolutionizing UV curing technology: IST America & INTECH collaborate at RadTech
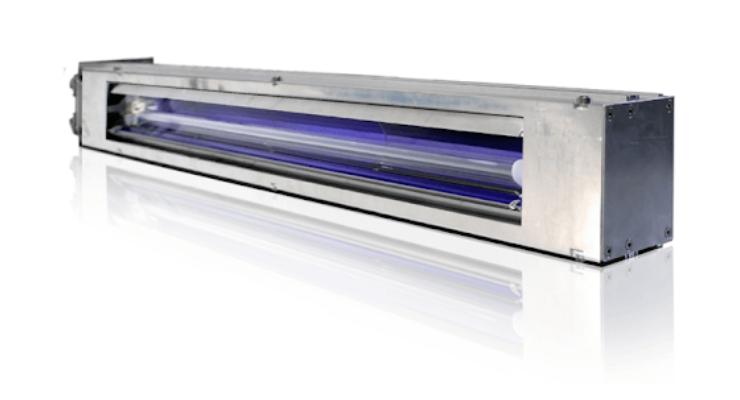
IST America (ISTA) is excited to be participating in the upcoming RadTech UV&EB Technology & Conference in Orlando, FL from May 20-22. At the conference, they will showcase their UV,…
WHO Scales Up Mental Health Support for Armenian Refugee Population through Mobile Teams and Hotlines
The World Health Organization (WHO) is dedicated to scaling up Mental Health and Psychosocial Support (MHPSS) services for Armenian refugee and host populations. Over the past six months, WHO has…
Tragic Death in Canton: The Dark Side of Police Custody and the Controversial Use of Face-Down Restraints
A resident of eastern Canton died in police custody last week after being handcuffed and left face down on the floor of a social club. The officers involved in the…
Fed’s Rate Cut Hopes Dash as Inflation Report Shows 2.7% Annual Rate
Despite the Federal Reserve’s aim of keeping inflation at 2%, recent reports have shown an annual rate of 2.7%. This has led to speculation that rate cuts may not be…
Scottish Conservative Party Launches No-Confidence Vote Against Chief Minister Yousaf: Implications for SNP and Scottish Politics”.
The Scottish Conservative Party has proposed a vote of no confidence against the Chief Minister of Scotland, Humza Yousaf. This is due to his unilateral decision to break the government…
CBS Sports Launches New 24-Hour Streaming Channel for UEFA Champions League Fans
Real Madrid player Jude Bellingham was seen celebrating during the UEFA Champions League quarter-final against Manchester City in a recent match. The excitement and energy of the game were captured…
Transform Your Business: Next Level Grant Program in West Monroe Launches with $500 and $250 Grants
The “Next Level Business Grant” program has been announced by Keep West Monroe Beautiful in collaboration with the City of West Monroe and the West Monroe West Ouachita Chamber of…
Rise in Violent Crimes in Chile: International Organized Crime Groups and Transnational Crime Solutions
Chile has experienced an alarming increase in violent crimes in recent years, with international organized crime groups playing a significant role. Groups such as the Tren de Aragua from Venezuela,…
TikTok’s Voluntary Suspension of Lite App in Europe: Balancing Rewards and Regulations
TikTok has voluntarily suspended its Lite app in Europe, which paid users to watch videos or recommend other users. The app was launched as a test in Spain and France…
Rev Up Your Training at the Oklahoma City Memorial Marathon Health and Fitness Expo”.
The Oklahoma City Memorial Marathon is just around the corner and before the races begin, participants and guests are encouraged to visit the Health and Fitness Expo at the Oklahoma…


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-12466528093-bb52afb615994ff8983eb8cf1482a15c.jpg)